XR Benefits Health Care Providers
The multifaceted healthcare industry is notorious for late adoption. Perhaps it’s for this reason why we find it intriguing that extended reality technology has been embraced by many different areas on both the healthcare provider and patient side so quickly. Below, we dive deeper into the ways healthcare providers utilize XR to their benefit:
Dynamic Learning & Immersive Training
Virtual & augmented reality are commonly used for training and education, and spans many verticals including healthcare. In this rigid industry, where compliance, accuracy and experience matters most, it is vital to be properly trained and that afterwards the training is retained. For medical students, much of anatomy is learned with textbooks or images, despite the studies that show this type of content leaves room for misunderstanding.
XR affords students hands-on training opportunities, allowing an enhanced understanding and greater retention of what is being learned in each module. A student presented with a tangible AR model of a human organ for example, can move, enlarge, splice through layers, and watch how an organ functions in real-time. Check out CodeTank’s demo of an AR lung here.
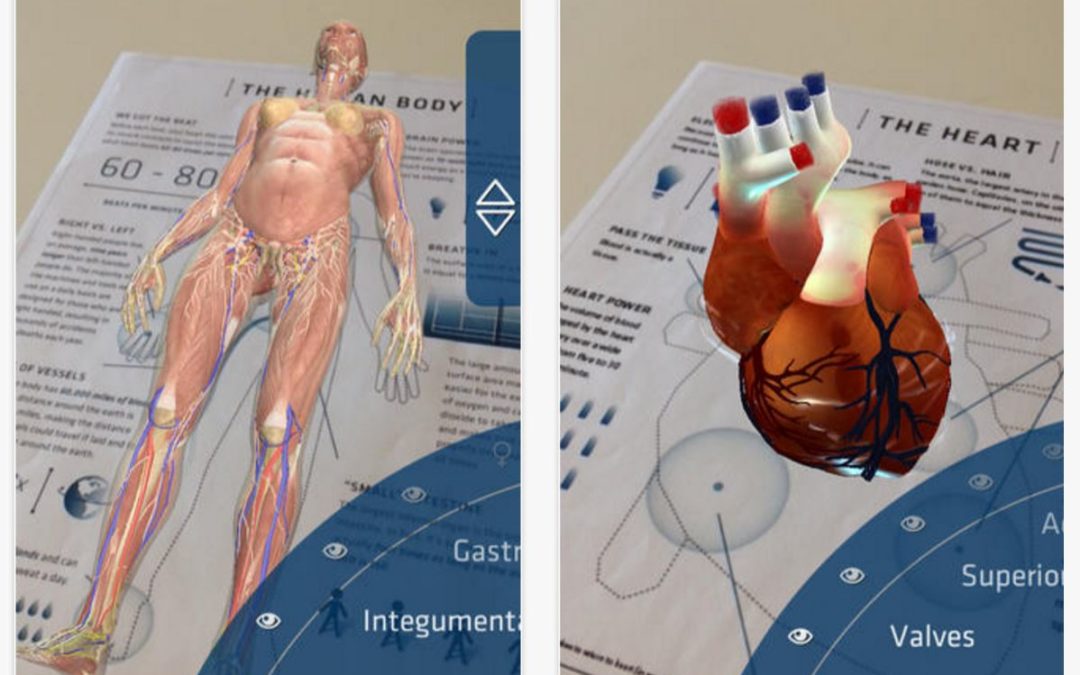
Aside from teaching anatomy, VR can be used to train new clinicians on basic procedures like inserting an IV, performing CPR, and wound care. Dr. Narendra Kini, CEO of Miami Children’s Health System, recently implemented VR training into Nicklaus Children’s Hospital. The benefit of the new training program has been unquestionable. Kini found that VR training retention levels can reach 80% after one year, compared to 20% retention levels after one week with conventional methods. VR training allows for repetitive learning of tasks that are otherwise difficult to perform repeatedly. Kini states,
We believe that there are numerous opportunities where repetitive training and skill set maintenance are critical for outcomes. Since there are not enough patients in many cases to maintain these skill sets, virtual reality is a real addition to the arsenal. Imagine also scenarios where we need to practice for accreditation and or compliance. In these situations virtual reality is a god-send.”
Strategic Planning
Planning a procedure is a necessary step in completing successful operations. With AR, surgeons no longer have to mentally “map out” these operations. In 2018, surgeons from the University of Texas Health Science Center were the first to use AR during an invasive procedure. With the help of AR, Dr. Martin J. Citardi and his team members developed a surgical plan for a patient’s sinuses. After planning, the operating team overlaid the AR images onto the surgeon’s endoscopic view. Citardi stated that, “ …3D mapping and imagery, enhances our understanding of complex anatomy so surgical procedures are more precise,” He later continued saying that the technology, “…offers patients the benefit of minimally invasive surgery with lower risks and better outcomes.”
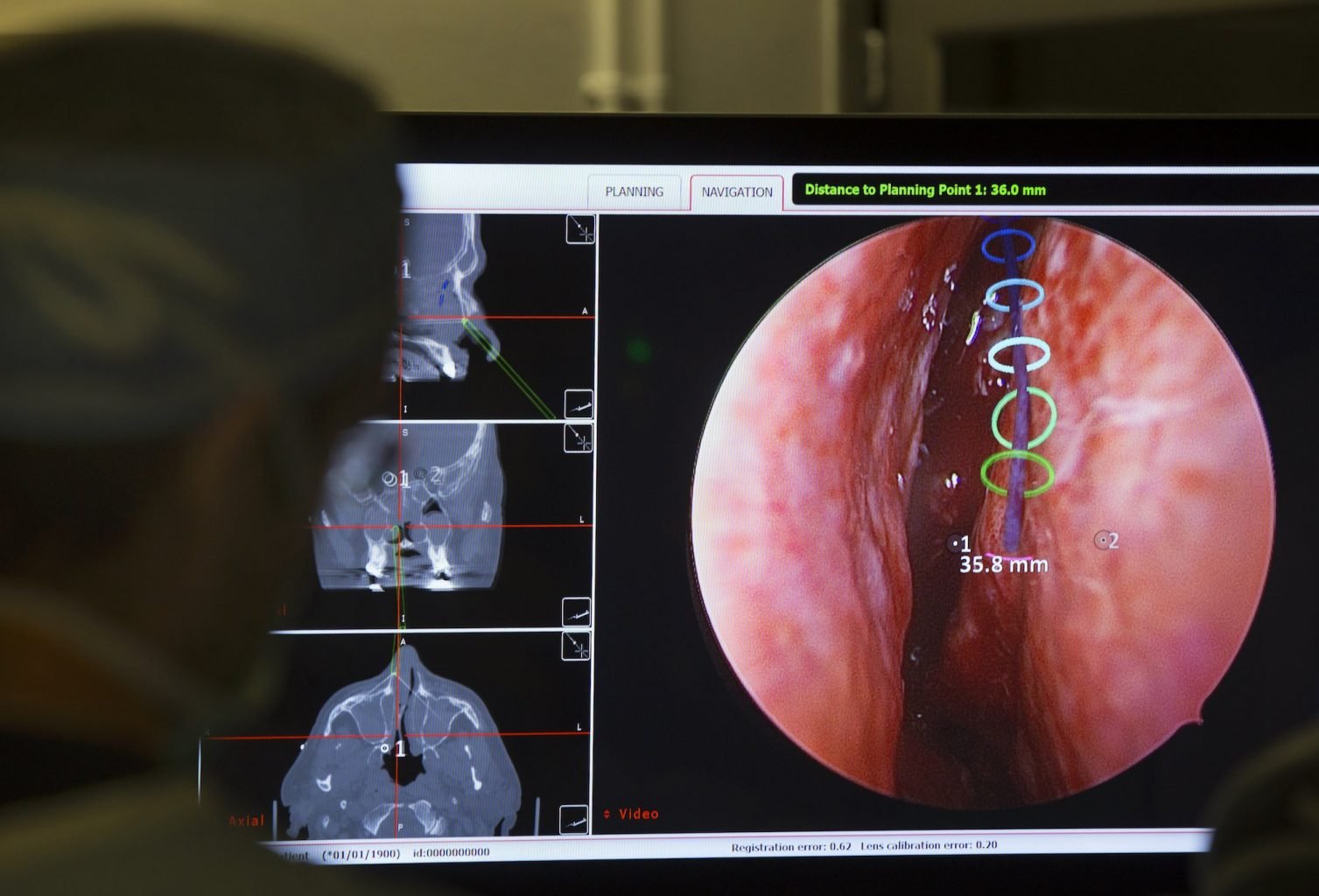
Virtual reality, not just augmented reality, is also making a splash in preoperative planning. A 2018 study from Stanford University found that VR imaging of increases radiologists’ confidence when planning a procedure. Dr. Zlatko Devcic of Stanford University says that VR imaging can, “…help interventional radiologists more quickly and thoroughly plan for the equipment and tools they’ll need for a successful outcome.” With this ability to thoroughly plan and create an operation roadmap, clinicians are able to execute a procedure with more confidence and precision.
VR is also being used by surgeons to routinely practice difficult surgeries with zero risk. They enable the surgeon to gain insight into all aspects of surgery, from patient interactions, to suturing an incision. Stanford states that [XR] training/practice provides surgeons with, “…realistic sights, sounds, and forces like they were actually in the operating room.” It’s clear to see that XR can be the new technology that trains healthcare professionals of the future.
Heightened Safety
Mitigating risks before and during operations helps to prevent infection and surgical mistakes. With AR, surgeries are becoming less invasive, more streamlined, and, in certain instances, preventable. Augmedics is a company that develops augmented 3D visualizations of a patient’s spine. Surgeons are able to practically see through a patient’s skin, muscles, and other tissues, essentially giving the surgeon “x-ray vision.” This enables clinicians to make the operation as minimal and non-invasive as possible, thus increasing patient safety. Accuvein is another company that is making what is difficult to see, visible. Accuvein has developed a product that projects a patient’s veins on their skin, thus making it much easier to insert a needle. Accuvein states that their product allows for 45% fewer escalations and saves hundreds of thousands for healthcare providers.
Overall, immersive training, superior planning, and augmented visualizations evoke better understanding and confidence in a clinician. This then makes procedures quicker, simpler, and safer.
The integration of XR into the healthcare industry is exciting and beneficial to all parties. With the technology’s power, many facets of healthcare will be upgraded. XR can create long-lasting and effective medical solutions that will impact patients and providers alike. Curious to discover how AR and VR can impact your medical company? We want to hear from you!
To learn more, reach out to our team at CodeTank Labs here.
Written By: Ethan Rosas & Lauren McNamara @ CodeTank Labs
Sources:
Maddox, Todd. “How XR Technologies Will Accelerate Healthcare Training.” Main, 19 Sept. 2018, www.td.org/insights/how-xr-technologies-will-accelerate-healthcare-training.
“Using Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Realities for Medical Training.” Design Interactive, 22 Mar. 2018, designinteractive.net/using-virtual-augmented-mixed-realities-medical-training/.
“Surgical Simulation.” Salisbury Robotics Lab, web.stanford.edu/group/sailsbury_robotx/cgi-bin/salisbury_lab/?page_id=205.
“Here’s Why Hospitals Are Using Virtual Reality to Train Staff.” Fortune, fortune.com/2015/08/17/virtual-reality-hospitals/.
“Stanford Study Finds VR Imaging Boosts Radiologists’ Confidence.” MobiHealthNews, 19 Mar. 2018, www.mobihealthnews.com/content/stanford-study-finds-vr-imaging-boosts-radiologists-confidence.
Wagenen, Juliet Van, et al. “Healthcare Teams Gain Edge by Using VR, AR for Surgery, Training.” Technology Solutions That Drive Healthcare, healthtechmagazine.net/article/2018/04/Healthcare-Teams-Gain-Edge-by-Using-VR-AR-for-Surgery-Training.
“Texas Surgeons Perform First Sinus Surgery Using AR.” MobiHealthNews, 14 Mar. 2018, www.mobihealthnews.com/content/texas-surgeons-perform-first-sinus-surgery-using-ar.
“Evidence For Vein Visualization As The Standard Of Care.” AccuVein, dd2.2b0.myftpupload.com/evidence/.
“Gaming Tech and 3-D Are Changing the OR.” TMC News, 29 July 2018, www.tmc.edu/news/2018/05/gaming-tech-and-3-d-reach-the-or/.
“5 Ways Virtual Reality Is Disrupting the Healthcare Industry.” XRHealth, www.xr.health/virtual-reality-disrupting-healthcare.html/.
